Theory
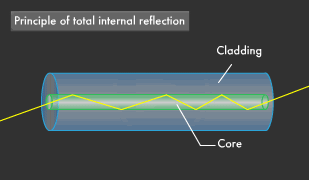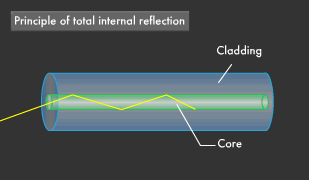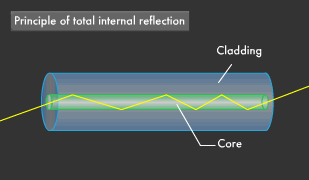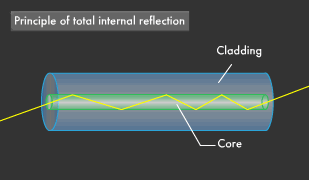
Optical fibres works on the principle of total internal reflection. When light ray strikes at the internal surface
of optical fibre cable called such that incidence angle is greater than critical angle,
then incident light ray reflects in the same medium and this phenomenon repeats.
In this way a light signal travels from one end of the cable to another end. Beyond a certain angle, the refraction will cause light to be reflected from the surface.
Optical fiber uses this reflection to "trap" fiber in the core of the fiber by choosing core and cladding materials
with the proper index of refraction that will cause all the light to be reflected if the angle of the light is below a certain angle.
We call that "total internal reflection."
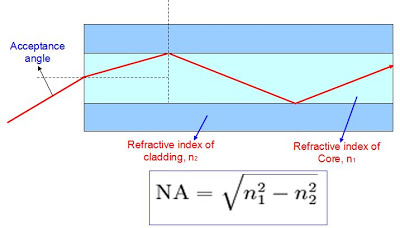
Numerical Aperture =
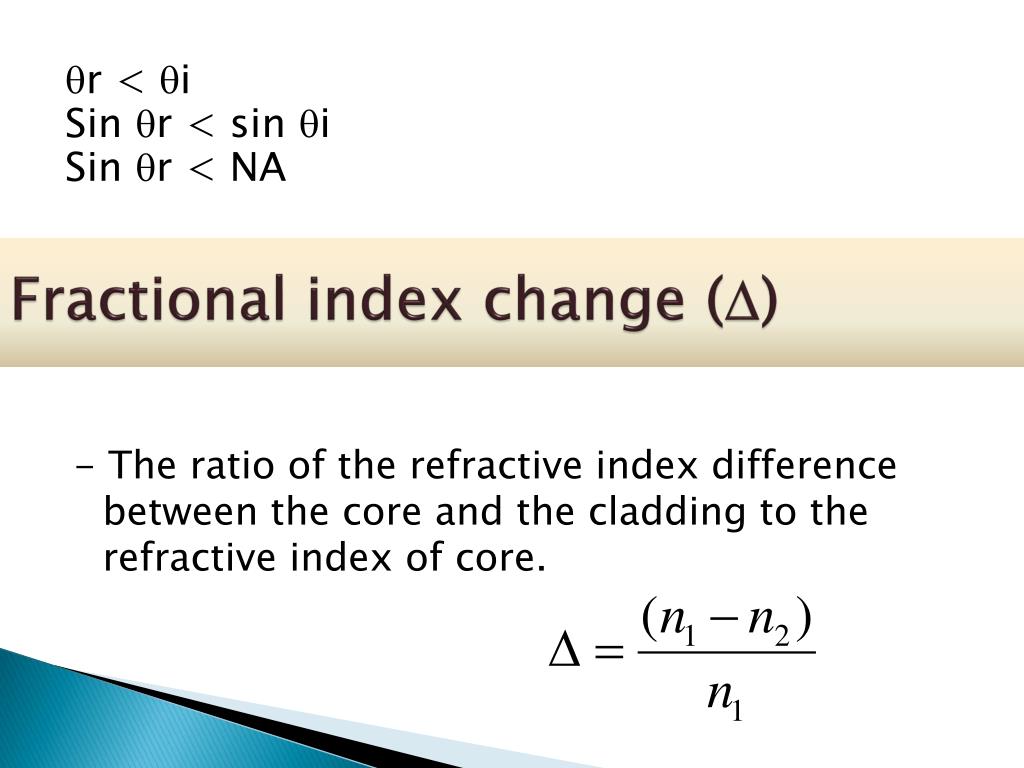
Fractional Index Change =
Critical Angle = sin-1( )
Critical Angle = sin-1( )
